Intelligently Connecting Data and Insight to Navigate the Clinical Research Trends of Tomorrow
Advancing health is all about connections. Connecting people, data, insights, and technology for a better, more efficient clinical trial experience. So as the calendar turns over to another year, we’ve asked our scientific and subject matter experts to connect our data with their expertise and share their thoughts about what trends, changes, and innovations they are looking forward to in 2024 and beyond.
While the industry continues to adjust in a post-COVID world, as of this publication we expect clinical trial starts in 2024 to be up slightly over 2023. Despite this improvement, disconnects remain. Sites continue to struggle with resourcing and the demands of working in multiple technology platforms. Sites, sponsors, and CROs are working to bridge the gap between artificial intelligence, machine learning, drug development, and decision making. All stakeholders are focusing on the continued promise of digital health tools that provide researchers with real-time data, as well as new approaches to clinical trials that prioritize the needs of participants first – beyond the protocol.
Below, our experts will connect you with insights to prepare you for what we expect to be another progressive year in the industry.
Diversity, Equity & Inclusion
Decentralized & Hybrid Trials
Research Site Readiness
Emerging Opportunities
Diversity, Equity & Inclusion
Lack of diversity in clinical trials can impair quality, increase costs, and put patient safety at risk. Many therapies work differently depending on a person’s gender, race, and ethnicity, so without diverse participants, scientists and clinicians have only a limited understanding of the effectiveness and suitability of treatments for underrepresented populations.
These critical differences are eventually discovered — after the therapeutic has been approved and is in widespread use. The barriers to diversity have been well-documented, but despite significant progress, the industry still struggles to overcome them.
While everyone agrees on the importance of diversity in clinical trials, the 2021 WCG Avoca State of the Industry Report: Diversity in Clinical Research Execution and Participation report found that respondents who saw the pursuit of diversity as a scientific or ethical imperative felt more strongly about its importance than those who considered diversity to be important primarily for regulatory or marketing reasons.

The scientific case for diversity is largely settled. What’s left is continuing to make the case with key stakeholders in moving DEI initiatives for clinical trials forward in a meaningful way. In this section, our experts will make the case for the significance of DEI in rare disease clinical trials.
Featured Insight
Current Opportunities and Outcomes in Rare Disease Clinical Trials
Decentralized & Hybrid Trials
The COVID-19 pandemic drove interest in decentralized (DCT) and hybrid trials. As the world emerges from the global pandemic, the utility of DCT elements continues as DCT and hybrid trials enable the delivery of a more participant-centric approach to research, as treatments can be delivered remotely, sponsors can engage with a more diverse patient population, and recruitment efforts can be accelerated.
But while digital devices, mobile applications, and online communication methods are useful tools, they are not complete solutions. The launch of Apple’s ResearchKit facilitated the enrollment of thousands of participants into research programs on a wide variety of chronic diseases, but several weeks later, about 90% of initial enrollees had dropped out of the project. As such, it’s important for the industry to determine the right mix of virtual and on-site care.
From a regulatory perspective, if the protocol is designed as a DCT or a hybrid trial, some or all research activities may occur at locations that are not traditional clinical trial sites. For example, a local healthcare provider clinic, a mobile unit, or the participant’s house may serve as the location for some research activities.
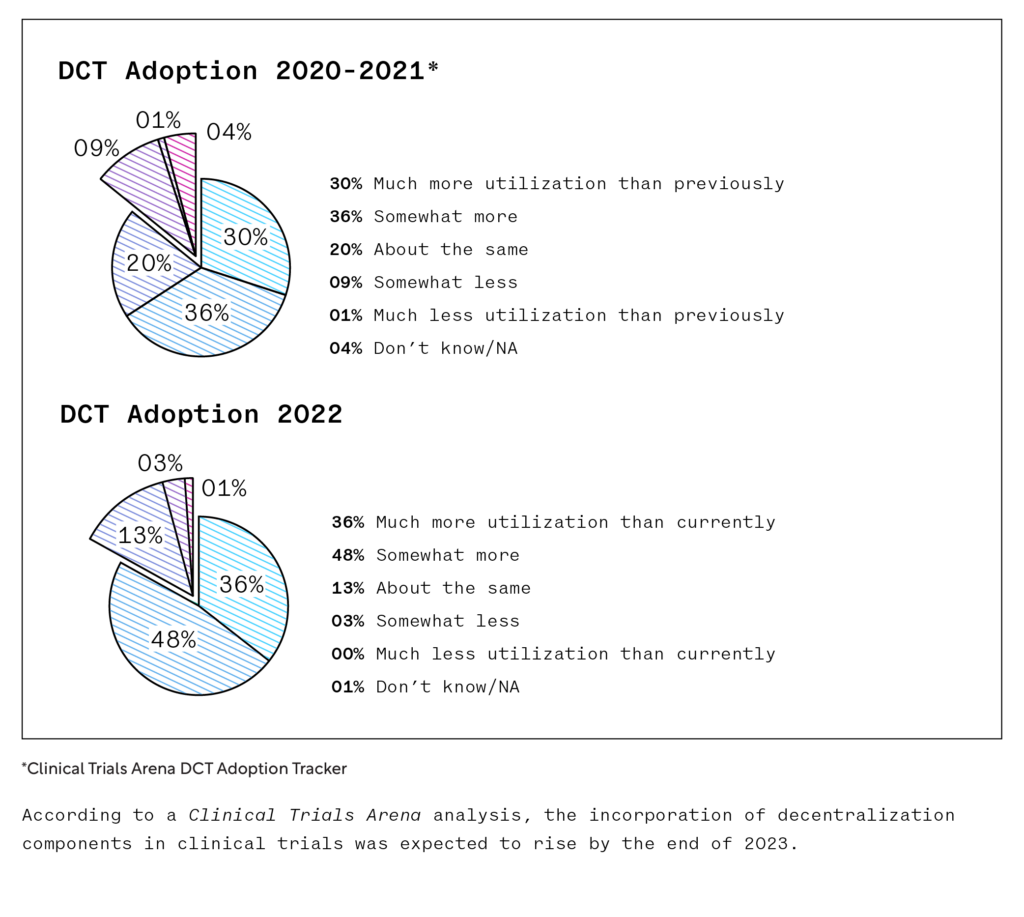
In 2023, the U.S. FDA issued its guidance on the design and implementation of DCTs and updated its position on using electronic systems, electronic records, and electronic signatures in clinical investigations. In addition to guidance development, the FDA has created a framework that includes workshops, demonstration projects, stakeholder engagement, a website, and internal processes to evaluate decentralized and virtual trials.
In this section, our expert outlines the impact of DCTs and hybrid trials on vaccines, and how we can continue to bring the promise of more patient-centric care through the enablement of DCTs.
Featured Insight
The Decentralization of Vaccines in 2024 and Beyond
Research Site Readiness
The evolution of clinical research has been dependent on the conversion of Healthcare Organizations (HCOs) to clinical research sites, along with the conversion of Healthcare Providers (HCPs) to Principal Investigators (PIs).
These conversions are critical to advancing medicine and providing cutting-edge treatment to patients. However, the current clinical research landscape has become increasingly intricate due to complex protocols, demanding data collection needs, and constricted study timelines, causing a slowdown in the conversion of HCOs and HCPs. As a result, the number of clinical trials now being initiated exceeds the amount of clinical research sites available to conduct these trials.
Because of this, active clinical research sites have become saturated and are facing unrelenting pressure to meet protocol endpoints within the timelines dictated. With only 15% of HCOs conducting clinical research according to industry sources, sponsors and CROs must ensure existing study sites are fully enabled to conduct efficient studies so protocol endpoints can be successfully met. To do this, sponsors and CROs must enable their study sites from the very beginning. Effective site enablement must address several key factors, including protocol design, training, participant recruitment and enrollment, and more.
Likewise, sites can optimize and grow their research businesses by harnessing solutions that improve site capacity, reduce start-up delays, and lessen their administrative burden. By leveraging site enablement solutions, sites can increase operational efficiency, recruit, and retain more participants sooner, deliver quality data, and improve their financial performance.
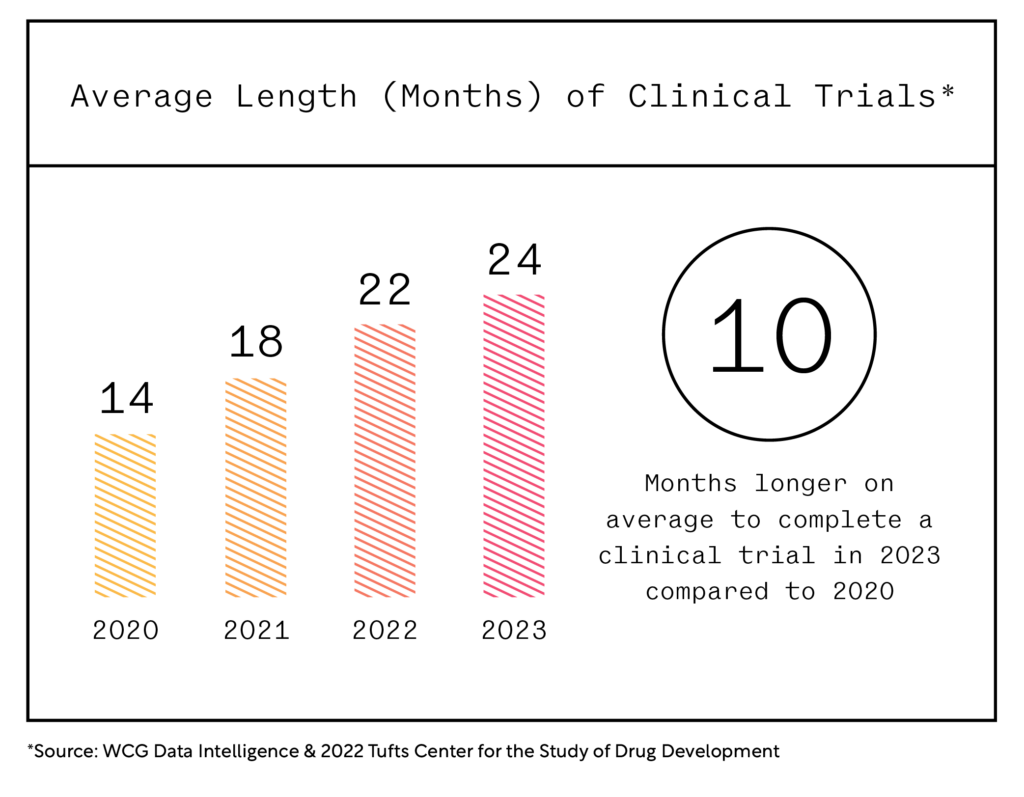
Read on for insights into how sponsors and CROs can better enable the research sites conducting their studies and how sites can address site capacity constraints.
Featured Insights
A Look Ahead: Site Trends for 2024
Recapturing the Progress Made with CTA Negotiations During the Pandemic
Site Readiness in Vaccine Trials: Lessons Learned from the COVID-19 Pandemic
Patient Recruitment Barriers in Oncology
Emerging Areas of Interest
Artificial Intelligence
The reach and impact of artificial intelligence (AI) throughout the healthcare industry has been steadily growing. From disease diagnosis to the tailoring of treatment plans, AI is starting to appear everywhere. But where is AI’s place in clinical trials?
According to the Tufts Center for the Study of Drug Development, a typical Phase III clinical trial generates more than 3.5 million data points. This finding highlights the need for artificial intelligence to manage these massive data sets to deliver insights for better, more timely decision making.
From a regulatory perspective, in 2023 the FDA published a discussion paper outlining the current and future applications of AI and machine learning (ML) in drug development. This paper addressed core issues like human-led governance, data quality, and model development standards. It emphasized a risk-based approach tailored to AI/ML use, emphasizing the importance of accountability and transparency. The FDA is requesting stakeholder feedback to help inform future regulatory activities. It is anticipated that AI will impact all areas of clinical research including protocol development and ethical review of research.
Digital biomarkers
Digital biomarkers are behavioral and physiological data such as heart rate, physical activity, and step counts collected using digital devices. These measurements can be reflective of treatment response, enabling a better understanding of disease progression, and they have the potential to replace time-consuming assessments that can be difficult for patients.
While this technological shift could introduce risks to clinical trials, it offers long-term benefits to patients and researchers alike when safely developed, assessed, and adopted.
Psychedelics
A recent search of clinicaltrials.gov found nearly 200 clinical trials of psychedelics currently registered. The FDA published its first draft guidance on this topic in 2021, and an expanding body of research suggesting that psychedelics may treat CNS disorders like substance abuse, depression, chronic pain, and schizophrenia has sparked a renewed interest in recent years by drug developers and investors.
This emerging area of research presents exciting opportunities to address important unmet medical needs for many disorders, including CNS. While there are some significant challenges, the potential to make significant strides in improving patients’ lives provides a sense of optimism for the future of the field.
Read on as our experts dive deeper into these emerging areas of opportunity.